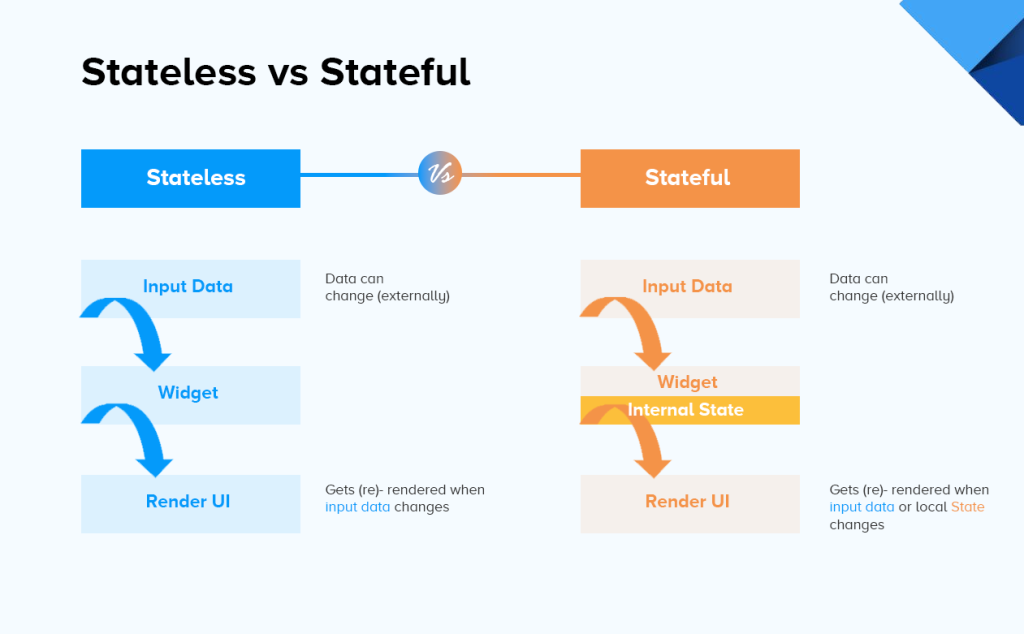
In Flutter, widgets are the building blocks of the user interface, and they can be broadly categorized into two main types: StatelessWidget and StatefulWidget. These widgets serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics:
StatelessWidget:
A StatelessWidget is a widget that doesn’t have mutable state. Once created, its properties (data) cannot change. Stateless widgets are typically used for presenting static or unchanging content. Key features of StatelessWidget:
Immutable: A StatelessWidget is immutable, meaning its properties are set during construction and cannot be modified afterward.
Build Method: Stateless widgets have a build method that is called once when the widget is created. It returns a widget tree that represents the user interface.
Rebuild on Parent Change: Stateless widgets can rebuild when their parent widget rebuilds, but they do not store their own state information.
Example Use Cases:
- Displaying text or images.
- Creating buttons with fixed labels.
- Representing static content like headers or footers.
class MyStatelessWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
child: Text('Hello, World!'),
);
}
}
StatefulWidget:
A StatefulWidget, on the other hand, is a widget that can change its properties (data) over time. It has associated mutable state that can be modified, and when the state changes, the widget rebuilds to reflect those changes. Key features of StatefulWidget:
Mutable State: StatefulWidget has an associated State object that can hold mutable data.
Build Method: Similar to StatelessWidget, StatefulWidget also has a build method to describe the widget’s user interface. However, this method can be called multiple times as the widget’s state changes.
State Rebuild: When the widget’s state changes (typically through user interactions or data updates), the build method is called again to update the UI.
Example Use Cases:
- Forms and input fields that need to reflect user input.
- Animated widgets that change appearance over time.
- Any widget that requires dynamic data updates.
class MyStatefulWidget extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_MyStatefulWidgetState createState() => _MyStatefulWidgetState();
}
class _MyStatefulWidgetState extends State<MyStatefulWidget> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: <Widget>[
Text('Counter: $_counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
The key difference between StatelessWidget and StatefulWidget in Flutter is the presence of mutable state. Use StatelessWidget when your UI remains static or unchanging, and use StatefulWidget when your UI needs to reflect changes in data or user interactions. Understanding this distinction is crucial for designing effective and efficient Flutter applications.