When your Laravel application starts growing, traffic is no longer just a number — it becomes a test of architecture.
Many teams think scaling means “upgrading the server.”
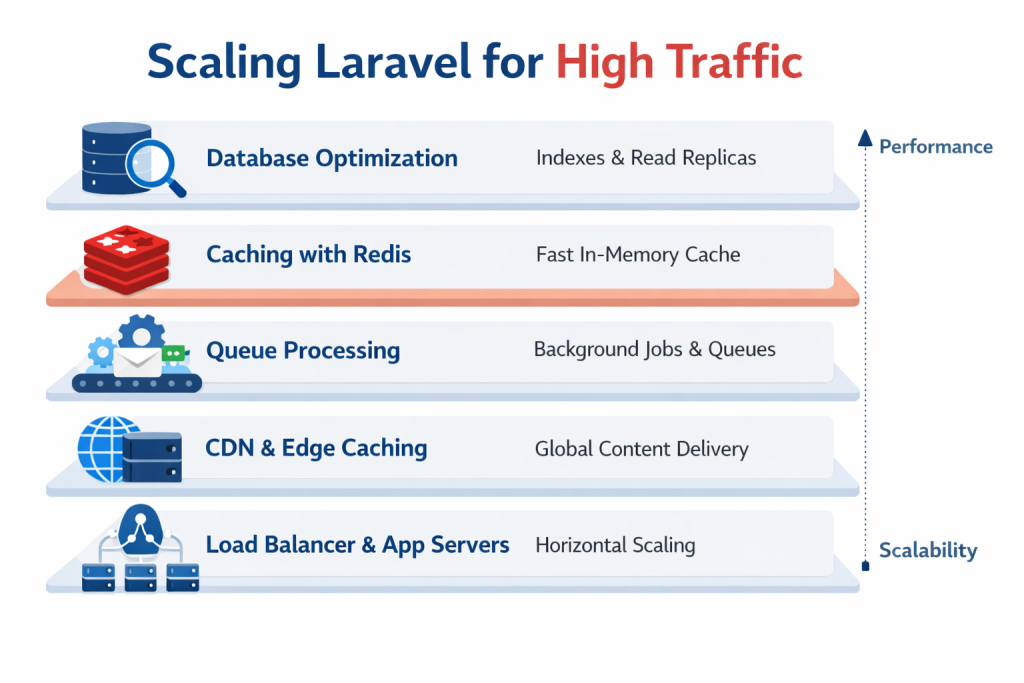
In reality, scaling Laravel for high traffic is about removing bottlenecks layer by layer.
In this detailed guide, we’ll walk through:
- Database optimization
- Caching strategies
- Queue architecture
- CDN & asset optimization
- Horizontal scaling
- Monitoring & observability
- Advanced performance tuning
Whether you’re running a startup SaaS, marketplace, booking platform, or enterprise application — this guide will help you scale confidently.
1️⃣ Understanding Where Laravel Applications Break
Before scaling, you must understand where high-traffic issues usually happen.
Most Laravel apps fail because of:
- ❌ Unoptimized database queries
- ❌ N+1 query problems
- ❌ Heavy synchronous processing
- ❌ File-based sessions
- ❌ No caching strategy
- ❌ Single-server architecture
Scaling is not about complexity.
It’s about fixing fundamentals first.
2️⃣ Database Optimization: The Foundation of Scaling
Your database is almost always the first bottleneck.
🔹 Add Proper Indexes
If a column appears in:
WHEREJOINORDER BYGROUP BY
…it should likely be indexed.
Example:
Schema::table('orders', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->index(['status', 'created_at']);
});
Composite indexes help dramatically in high-traffic systems.
🔹 Eliminate N+1 Queries
Bad:
$users = User::all();
foreach ($users as $user) {
echo $user->posts;
}
Good:
$users = User::with('posts')->get();
Use eager loading everywhere.
🔹 Select Only Required Columns
Bad:
User::get();
Better:
User::select('id','name')->get();
Less data = faster response = lower memory usage.
🔹 Use Read Replicas
For large-scale systems:
- Primary DB → Handles writes
- Replica DB → Handles reads
Laravel supports read/write configuration natively.
This alone can double your scaling capacity.
3️⃣ Caching: The Immediate Traffic Multiplier
If you’re not using Redis, you’re leaving performance on the table.
🔹 Use Redis for:
- Application cache
- Sessions
- Queues
- Rate limiting
Update .env:
CACHE_DRIVER=redis
SESSION_DRIVER=redis
QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis
🔹 Cache Expensive Queries
Example:
$topEvents = Cache::remember('top_events', 600, function () {
return Event::where('status',1)->take(10)->get();
});
Now instead of 1000 DB hits, you get 1.
🔹 Cache Config & Routes
Always run in production:
php artisan config:cache
php artisan route:cache
php artisan view:cache
These small optimizations matter at scale.
4️⃣ Move Heavy Work to Queues
High traffic + synchronous processing = disaster.
Never send:
- Emails
- Notifications
- SMS
- Webhooks
- Image processing
…inside a request.
Instead:
SendEmailJob::dispatch($user);
Use:
- Redis
- Laravel Horizon (for monitoring)
- Separate queues (high / default / low priority)
This keeps your web requests fast and responsive.
5️⃣ Use CDN & Edge Caching
Static assets should NEVER hit your application server repeatedly.
Use:
- Cloudflare
- AWS CloudFront
- Fastly
Benefits:
- Reduced server CPU load
- Faster global delivery
- Built-in DDoS protection
Add proper headers:
return response($content)
->header('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=600');
6️⃣ Make Your Application Stateless
To scale horizontally, your app must be stateless.
Do NOT use:
- File sessions
- Local storage for uploads
- Local cache drivers
Use:
- Redis sessions
- S3-compatible storage
- Centralized cache
This allows you to add more app servers behind a load balancer.
7️⃣ Horizontal Scaling Architecture
Basic high-traffic architecture:
Load Balancer
↓
Multiple Laravel App Servers
↓
Redis Cluster
↓
Primary Database
↓
Read Replica(s)
Now you can:
- Add more servers during traffic spikes
- Handle Black Friday–style events
- Avoid single points of failure
8️⃣ PHP & Server-Level Optimization
🔹 Use Nginx + PHP-FPM
Tune PHP-FPM:
pm = dynamic- Adjust
pm.max_childrenbased on RAM - Enable OPcache
🔹 Enable OPcache
This reduces PHP parsing time dramatically.
🔹 Increase Realpath Cache
Improves file lookup performance.
9️⃣ Monitoring & Observability
Scaling without monitoring is gambling.
Track:
- Response time (p95 & p99)
- Slow queries
- Queue wait time
- Memory usage
- Cache hit ratio
Tools:
- Laravel logs
- Database slow query log
- New Relic / Datadog / Elastic APM
- Horizon dashboard
What gets measured gets improved.
🔟 Laravel Octane (Advanced Optimization)
When you’re ready for serious throughput:
Laravel Octane (Swoole / RoadRunner)
Benefits:
- Keeps app in memory
- Removes repeated bootstrapping
- Significantly increases requests per second
Important:
You must avoid shared state issues.
Octane is powerful — but should be implemented carefully.
Common Mistakes When Scaling Laravel
❌ Throwing bigger servers at bad queries
❌ Ignoring indexing
❌ Running heavy logic in Blade loops
❌ Using file sessions in production
❌ No caching strategy
❌ No rate limiting
A Simple Scaling Roadmap
Phase 1
- Optimize queries
- Add indexes
- Enable Redis
Phase 2
- Move heavy tasks to queues
- Add CDN
- Cache frequently accessed pages
Phase 3
- Add multiple app servers
- Implement read replicas
- Improve observability
Phase 4
- Consider Octane
- Consider microservices (only if necessary)
Final Thoughts
Laravel scales extremely well — when designed properly.
Scaling is not about complexity.
It’s about eliminating bottlenecks, one layer at a time.
If your application is growing fast, now is the time to:
- Audit your database
- Implement Redis
- Move heavy processes to queues
- Add proper monitoring
Because when traffic spikes, architecture decides survival.