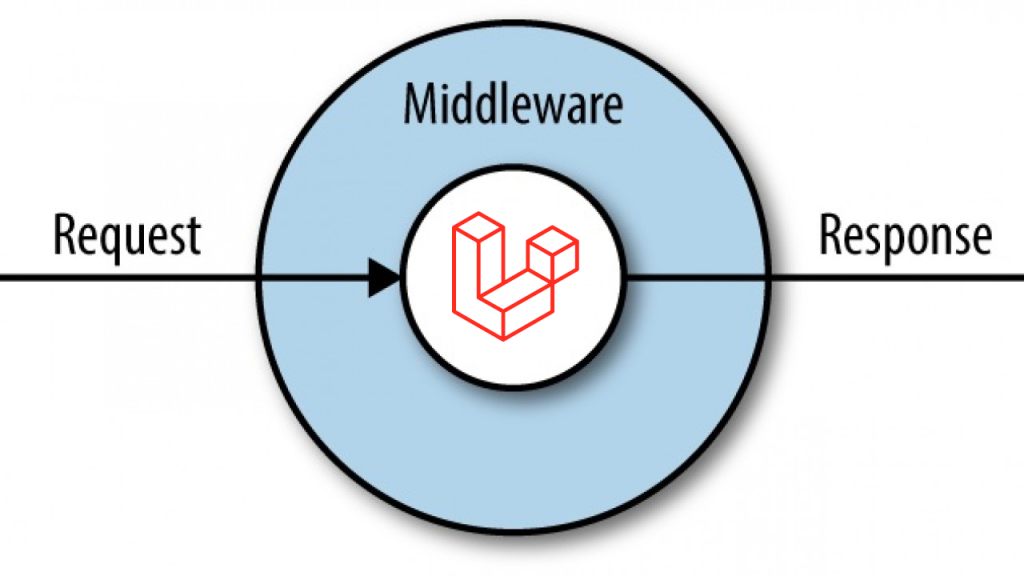
In Laravel, middleware plays a crucial role in handling HTTP requests and responses. It acts as a filter between incoming requests and the application’s routes, allowing you to perform tasks such as authentication, authorization, logging, and more.
What is Middleware?
Middleware is a mechanism in Laravel that intercepts HTTP requests entering your application and provides a convenient way to filter and manipulate them before they reach the intended route handler. It sits between the client’s request and the application’s response, allowing you to perform tasks at various stages of the request lifecycle.
Importance of Middleware
Middleware offers several benefits:
- Modularization: Middleware allows you to modularize common tasks, such as authentication and logging, and reuse them across multiple routes without duplicating code.
- Security: Middleware can enforce security measures by verifying authentication credentials, authorizing user access to routes, and protecting sensitive endpoints.
- Request Manipulation: Middleware enables you to modify incoming requests, such as adding headers, validating input data, or transforming request parameters.
- Response Manipulation: Similarly, middleware can manipulate outgoing responses, such as modifying headers, formatting data, or handling errors.
Creating and Using Middleware in Laravel
Creating middleware in Laravel is straightforward:
Generate Middleware: You can generate a new middleware using the make:middleware Artisan command:
php artisan make:middleware MyMiddleware
Define Middleware Logic: Implement the middleware logic within the handle method of the generated middleware class.
Register Middleware: Register the middleware in the $middleware property of the App\Http\Kernel class. This determines the global middleware stack or assigns middleware to specific routes or route groups.
Attach Middleware to Routes: Attach the middleware to routes or route groups using the middleware method in your route definitions.
Example: Creating Authentication Middleware
Let’s create a simple authentication middleware to protect certain routes from unauthorized access:
Generate the middleware:
php artisan make:middleware Authenticate
Implement the middleware logic:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class Authenticate
{
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next)
{
// Check if the user is authenticated
if (!auth()->check()) {
return redirect()->route('login');
}
return $next($request);
}
}
Register the middleware in App\Http\Kernel:
protected $routeMiddleware = [
// Other middleware...
'auth' => \App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
];
Attach the middleware to routes:
Route::get('/dashboard', function () {
// Dashboard route logic...
})->middleware('auth');